January 6, 2025
Pill Generic
Say Goodbye to Synthetic Drugs: Effective Natural Antibiotics for Healing
Antibiotics revolutionized medicine, but overuse of synthetic Antibiotics has led to concerns about side effects, resistance, and gut health. Natural antibiotics offer a gentler alternative for treating mild infections and boosting immunity while avoiding synthetic drug complications. Here’s a look at some of the most effective natural antibiotics, their benefits, and how to use them safely.



What Are Natural Antibiotics?
Natural antibiotics are substances derived from plants, herbs, and natural compounds that have antibacterial, antiviral, or antifungal properties. They can combat harmful microorganisms while being gentler on the body.Effective Natural Antibiotics for Healing
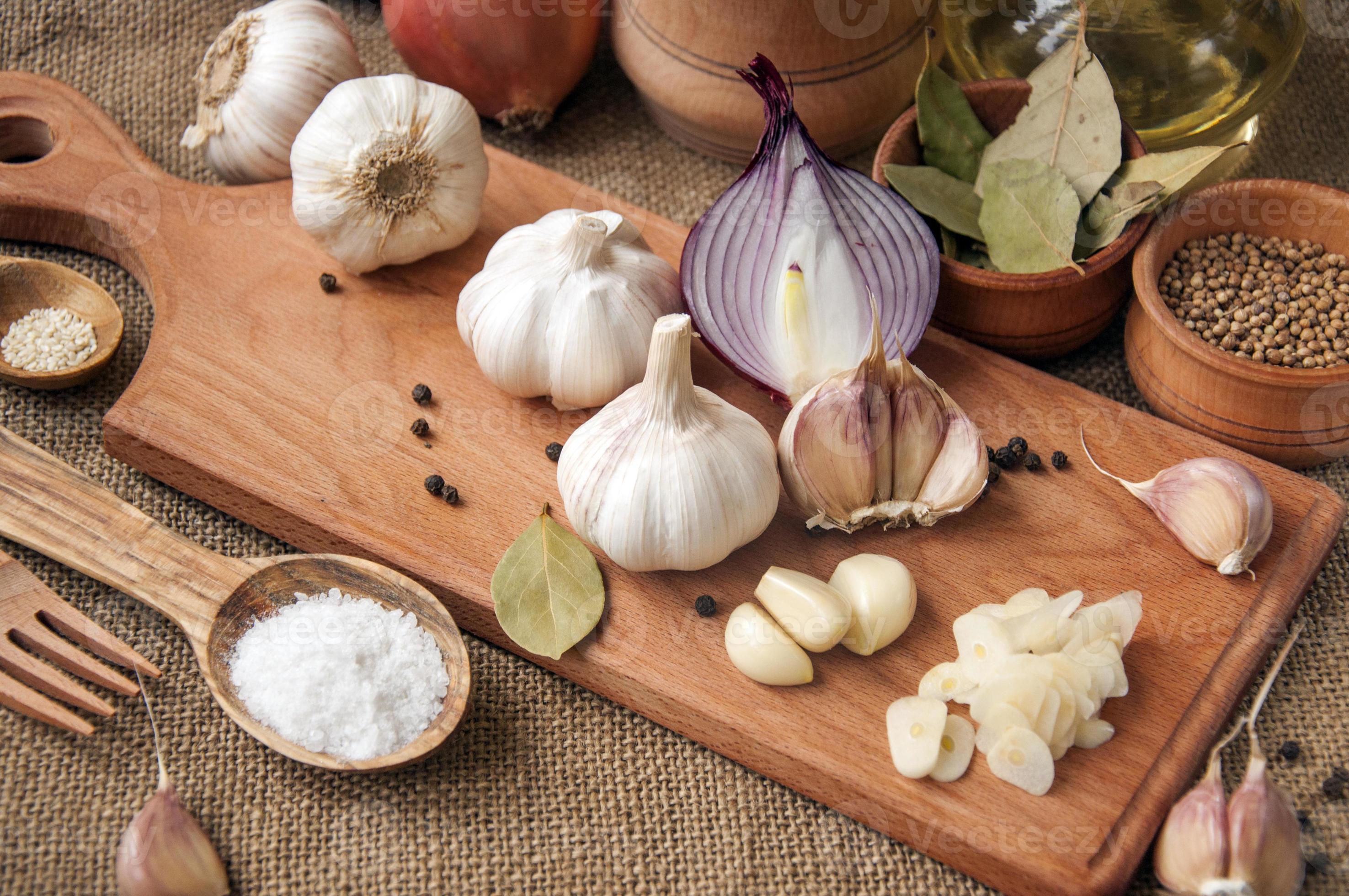
1. Garlic
- Active Ingredient: Allicin.
- Benefits:
- Broad-spectrum antibacterial and antiviral properties.
- Effective against E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and fungal infections.

- How to Use:
- Eat raw garlic or take garlic supplements.
- Crush and mix with honey for a natural antibiotic paste.
2. Manuka Honey
- Active Ingredient: Methylglyoxal (MGO).
- Benefits:
- Powerful antibacterial properties.
- Promotes wound healing and prevents infection.
- How to Use:
- Apply directly to wounds.
- Consume a teaspoon daily to boost immunity.
3. Ginger
- Active Ingredients: Gingerol and shogaol.
- Benefits:
- Effective against respiratory and gastrointestinal infections.
- Combats drug-resistant bacteria.
- How to Use:
- Brew ginger tea or consume fresh ginger slices.
- Use powdered ginger as a spice in meals.
4. Oregano Oil
- Active Ingredient: Carvacrol.
- Benefits:
- Potent antimicrobial against bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
- Supports gut health by targeting harmful bacteria.
- How to Use:
- Take diluted oregano oil orally (1–2 drops in a glass of water).
- Use as a topical treatment for fungal infections.
5. Turmeric
- Active Ingredient: Curcumin.
- Benefits:
- Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Helps prevent infection in wounds and promotes healing.
- How to Use:
- Mix turmeric with warm milk or water.
- Apply a turmeric paste to wounds.
6. Echinacea
- Active Compounds: Polysaccharides and alkamides.
- Benefits:
- Boosts the immune system.
- Effective against respiratory and urinary tract infections.
- How to Use:
- Take echinacea supplements or tea.
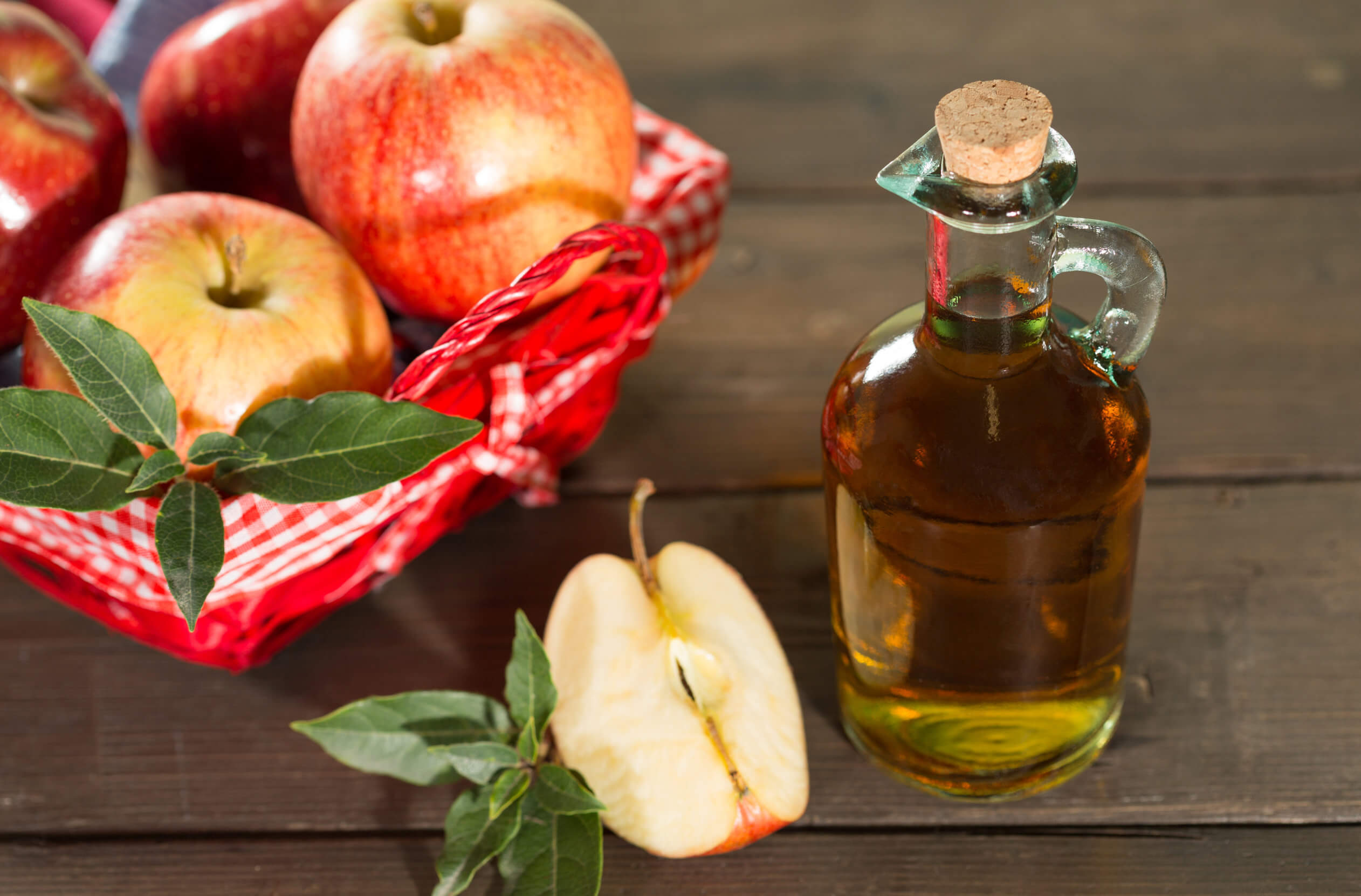
7. Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)
- Active Ingredient: Acetic acid.
- Benefits:
- Antimicrobial and antifungal properties.
- Supports digestive health.
- How to Use:
- Dilute 1–2 tablespoons in water and drink.
- Use as a topical rinse for skin infections.

8. Coconut Oil
- Active Ingredient: Lauric acid.
- Benefits:
- Fights bacterial, fungal, and viral infections.
- Soothes skin irritation.
- How to Use:
- Apply directly to the skin for infections.
- Use in cooking for daily antimicrobial benefits.
9. Cranberry
- Active Compounds: Proanthocyanidins.
- Benefits:
- Prevents urinary tract infections (UTIs) by stopping bacteria from adhering to bladder walls.
- How to Use:
- Drink unsweetened cranberry juice or take cranberry supplements.
10. Goldenseal
- Active Ingredient: Berberine.
- Benefits:
- Effective against bacterial and parasitic infections.
- Soothes respiratory and gastrointestinal issues.
- How to Use:
- Take goldenseal supplements.
- Use as a tea or topical application.
Precautions When Using Natural Antibiotics
- Use for Mild Infections:
- Natural antibiotics are best for non-severe infections or as preventative measures.
- Follow Dosages:
- Overuse of natural remedies can lead to side effects or reduced effectiveness.
- Consult a Doctor:
- Seek medical advice for persistent or severe infections.
- Ensure natural remedies won’t interfere with medications or medical conditions.
- Allergic Reactions:
- Test for allergies before using topical applications or consuming new natural antibiotics.

When to Consider Synthetic Antibiotics
While natural antibiotics can be effective for many conditions, synthetic antibiotics are often necessary for:- Severe bacterial infections like pneumonia or meningitis.
- Life-threatening conditions requiring immediate, targeted treatment.












 Supplement Safety Tips
Supplement Safety Tips





 FAQs
FAQs