About Acid Reducer
Acid reducers manage conditions like GERD, peptic ulcers, and gastritis. They are commonly prescribed. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) are popular acid reducers.
They work by targeting proton pumps in the stomach lining to lower acid production.
Acid reducers, or acid-suppressing meds, address stomach acid overproduction. This can lead to gastrointestinal ailments.
Acid reducers are medications that help control stomach acid.
They include Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) and Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists (H2RAs). These drugs work differently to reduce acid and .
This introduction explains acid reducers, their uses, and how they affect digestive health. To understand how these medications work, people can explore the details.
This will help them manage their digestive issues with knowledge and proactive strategies.
What Are Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)?
PPIs are drugs that reduce stomach acid by blocking proton pumps in the stomach lining. This helps relieve symptoms of acid reflux, heartburn, and related conditions.
Reducing acid production helps relieve symptoms of acid reflux, heartburn, and related issues.
PPIs are medicines that help lower stomach acid production.
Doctors often recommend them for conditions like GERD, peptic ulcers, and erosive esophagitis.
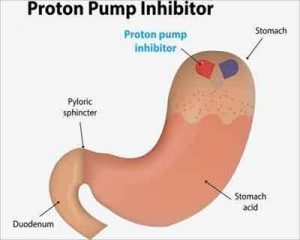
PPIs reduce stomach acid by stopping proton pumps in the stomach lining. This lowers the amount of hydrochloric acid produced in the stomach.
How Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) Work
PPIs reduce stomach acid by binding to proton pumps in the stomach lining cells.
PPIs reduce the amount of acid in the stomach by blocking certain pumps. This helps decrease the acidity of the stomach contents.
Proton pumps are enzymes found in the parietal cells of the stomach lining. Proton pumps are enzymes in the stomach lining that help produce stomach acid. This acid is necessary for digesting food and killing harmful
bacteria.
PPIs reduce stomach acid by attaching to and stopping the actions of proton pumps. This action cannot be reversed and leads to a big decrease in stomach acid production. PPIs lower gastric acidity. This alleviates heartburn, acid reflux, and esophageal inflammation.
PPIs are usually taken by mouth. It's important to think and watch closely with a healthcare professional.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) Use
Doctors often prescribe Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) to treat different stomach problems. They are important in managing a range of gastrointestinal conditions.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly prescribed for many stomach problems. They are crucial for treating conditions related to acid and supporting digestion.
Conditions Treated With PPIs:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (
GERD) is commonly treated with PPIs.
They help heal ulcers in the stomach and small intestine and reduce the chance of them coming back. By reducing gastric acid secretion, PPIs facilitate ulcer healing and help prevent recurrence.
Considerations for Long-Term Use:
PPIs are usually safe and effective for temporary relief of symptoms. These may include an increased risk of fractures.
Healthcare providers check the risks and benefits of long-term PPI use. They may suggest regular check-ups or other treatments as needed.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) are valuable for acid-related gastrointestinal disorders.
They offer a therapeutic option. Their effectiveness in providing relief and promoting healing is crucial in gastroenterology. It highlights their importance in modern medicine.
Judicious use and close monitoring are essential for optimal treatment outcomes. It helps minimize potential adverse effects associated with long-term PPI use. Patients need to communicate openly with healthcare providers for better digestive health management. It ensures comprehensive care.
Side Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
If you are taking PPIs, it's important to know about possible side effects. If you have any worrisome symptoms, talk to your healthcare provider.
Some common side effects of PPIs include:
Headache: Headaches are among the most commonly reported side effects of PPIs. Persistent or severe headaches should be checked by a doctor if they don't go away quickly.
Prolonged PPI use can cause vitamin B12 deficiency by impairing nutrient absorption. It leads to a deficiency in the essential nutrient. People on long-term PPIs should monitor vitamin B12 levels regularly. If deficiency is found, consider supplementation.
PPIs can raise the chance of getting a bacterial infection called Clostridium difficile. This infection causes severe diarrhea and colitis. People who had C. difficile in the past or are at high risk should Individuals with a history of C. Those with C. difficile infection should use PPIs cautiously and under supervision.
Prolonged use of PPIs can cause low levels of magnesium in some people. This can lead to issues like muscle cramps, tremors, and seizures. It is important to monitor the levels of magnesium in patients who use PPIs for a long time. This is recommended to ensure their well-being.
How to Take Acid Reducer
Using an acid reducer correctly is important. It helps it work well and lowers the chance of side effects.
Here are some guidelines on how to take an acid reducer:
1. Follow Healthcare Provider's Instructions:
Take the medicine as your doctor tells you or as it says on the label. Always follow their advice.
2. Swallow Whole:
Swallow the acid reducer tablets or capsules whole with water. Follow the instructions and do not crush, chew, or break them, as it may change how they work or upset your stomach.
3. Consider Special Instructions:
Some acid reducers, like delayed-release forms, need specific administration instructions. This timing helps the body utilize the medication effectively.
4. Monitor for Side Effects:
Common side effects may include headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea. If you experience persistent or severe side effects, notify your healthcare provider promptly.
5. Maintain Communication with Healthcare Provider:
Let your healthcare provider know about your experience with the acid reducer. Tell them about any changes in symptoms or side effects. Your healthcare provider can adjust the dosage or recommend alternative treatments if necessary.
6. Do Not Abruptly Stop Treatment:
Avoid abruptly discontinuing your acid reducer without consulting your healthcare provider. Sudden stopping of treatment can cause rebound acid and recurring symptoms. If you want to stop the medicine, talk to your doctor about slowly reducing the dosage.
7. Store Properly:
Keep it away from moisture, heat, and direct sunlight. Follow any specific storage recommendations provided on the medication packaging.
8. Attend Follow-up Appointments:
Make sure to go to your follow-up appointments with your doctor. They'll check if the acid reducer is working well and watch out for any problems or changes in your health.
Your doctor might change your treatment if needed, based on how Your doctor might change your treatment if the medicine isn't working for you.
Follow these guidelines, communicate with your healthcare provider, and optimize your acid reducer. It will promote better management of acid-related conditions.

FAQ - Acid Reducer
Q: What is an acid reducer?
An acid reducer is a medication that helps decrease the production of stomach acid.
Q: How does an acid reducer work?
Acid reducers work by blocking the production of acid in the stomach, which helps alleviate symptoms of acid reflux and heartburn.
Q:
What conditions can acid reducers treat?
Acid reducers are commonly used to treat conditions such as acid reflux, heartburn, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Q: Can acid reducers interact with other medications?
Yes, acid reducers, like PPIs, can interact with some medications. This can affect their absorption and efficacy. Consult a healthcare professional for drug interactions and therapeutic optimization.
Q: How can I minimize the side effects of acid reducers?
Consider lifestyle changes like diet, weight management, and stress reduction to reduce risks. This can help prevent acid reducer side effects.
Fact Box - Acid Reducer
There are two common types of medications used to treat certain medical conditions. The first type is called Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs). Examples of PPIs include
omeprazole otc.
Indications:
Treats GERD, peptic ulcers, erosive esophagitis, and related acid issues.
Potential side effects of acid reducers may include headache, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Prolonged use can increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies and respiratory infections.